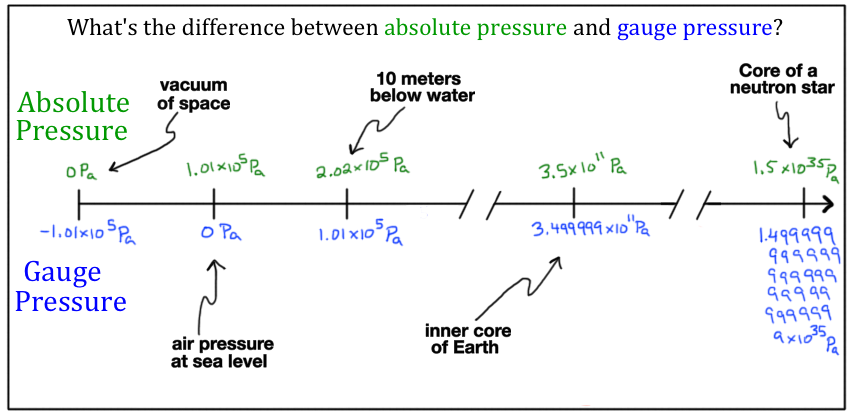
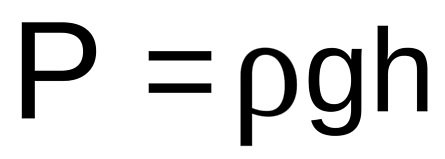homework and exercises - Why does P = $\rho$gh seem to contradict equal accelerations of fluids in a closed U tube? - Physics Stack Exchange
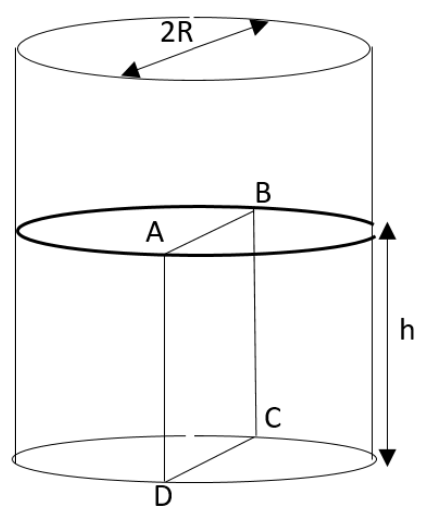
As shown in the diagram, water will be filled up to a height of $h$ in a beaker of radius $R$. The density of water is $\\rho $, the surface tension of
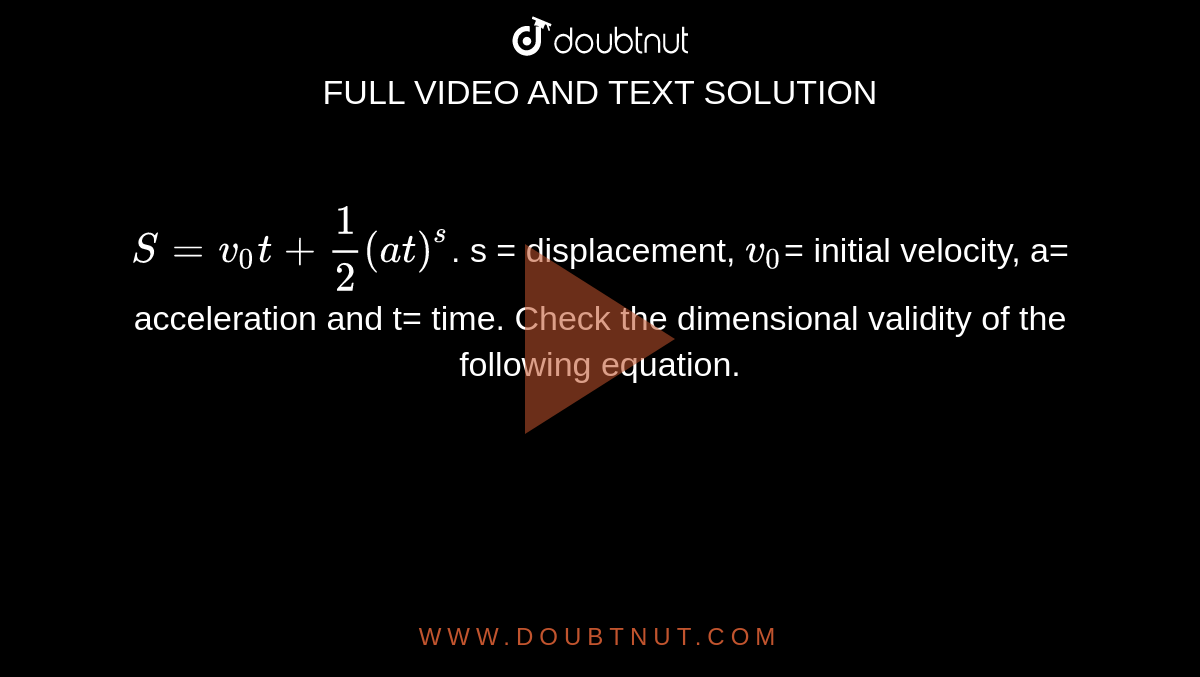
Which equation are dimensionally valid out of following equations (i) Pressure P= rho gh where rho= density of matter, g= acceleration due to gravity. H= height. (ii) F.S =(1)/(2) mv^(2)-(1)/(2) mv(0)^(2) where

Fluids and Elasticity Chapter 15. Density ( ) = mass/volume Rho ( ) – Greek letter for density Units - kg/m 3 Specific Gravity = Density of substance. - ppt download
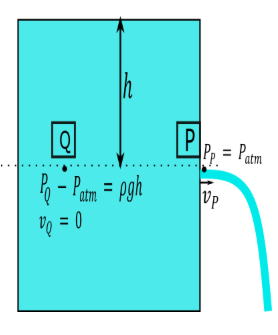
A leakage begins in the water tank at position P as shown in the figure. The initial gauge pressure at P was $5 \\times {10^5}N\/{m^2}$ .if the density of water is $1000kg\/{m^3}$

Fluids and Elasticity Chapter 15. Density ( ) = mass/volume Rho ( ) – Greek letter for density Units - kg/m 3 Specific Gravity = Density of substance. - ppt download
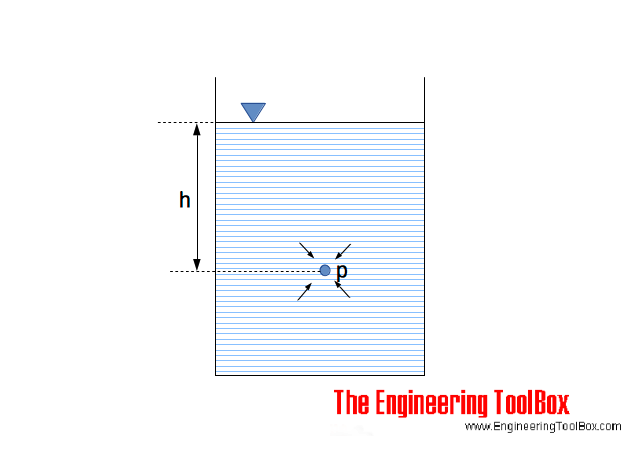
Is the equation [math]p=\rho gh[/math] the definition of hydrostatic pressure or just the equation from where we calculate it? - Quora

SOLVED: The pressure in fluid depends on both the density and the depth (h): P = pgh Using these relationships determine the atmospheric pressure at the following ocations Assume that atmospheric pressure