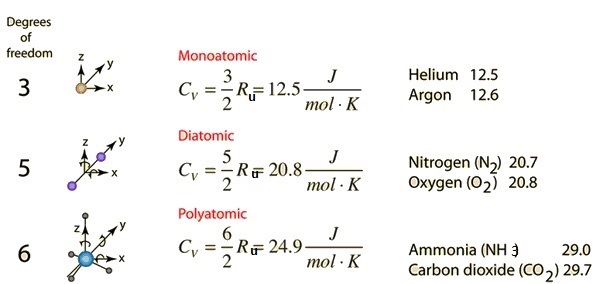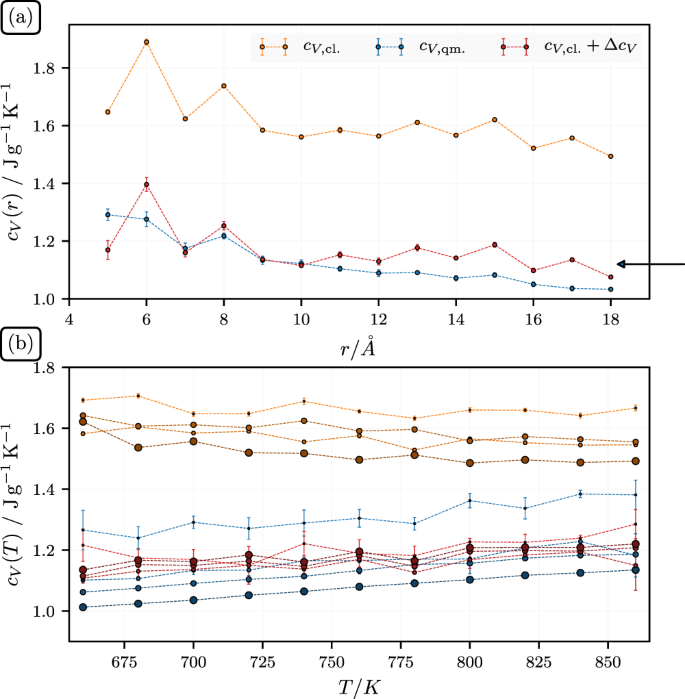
Specific heat capacity enhancement studied in silica doped potassium nitrate via molecular dynamics simulation | Scientific Reports

Molar Heat Capacity at Constant Volume for Isobutane at Temperatures from (114 to 345) K and at Pressures to 35 MPa | Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data
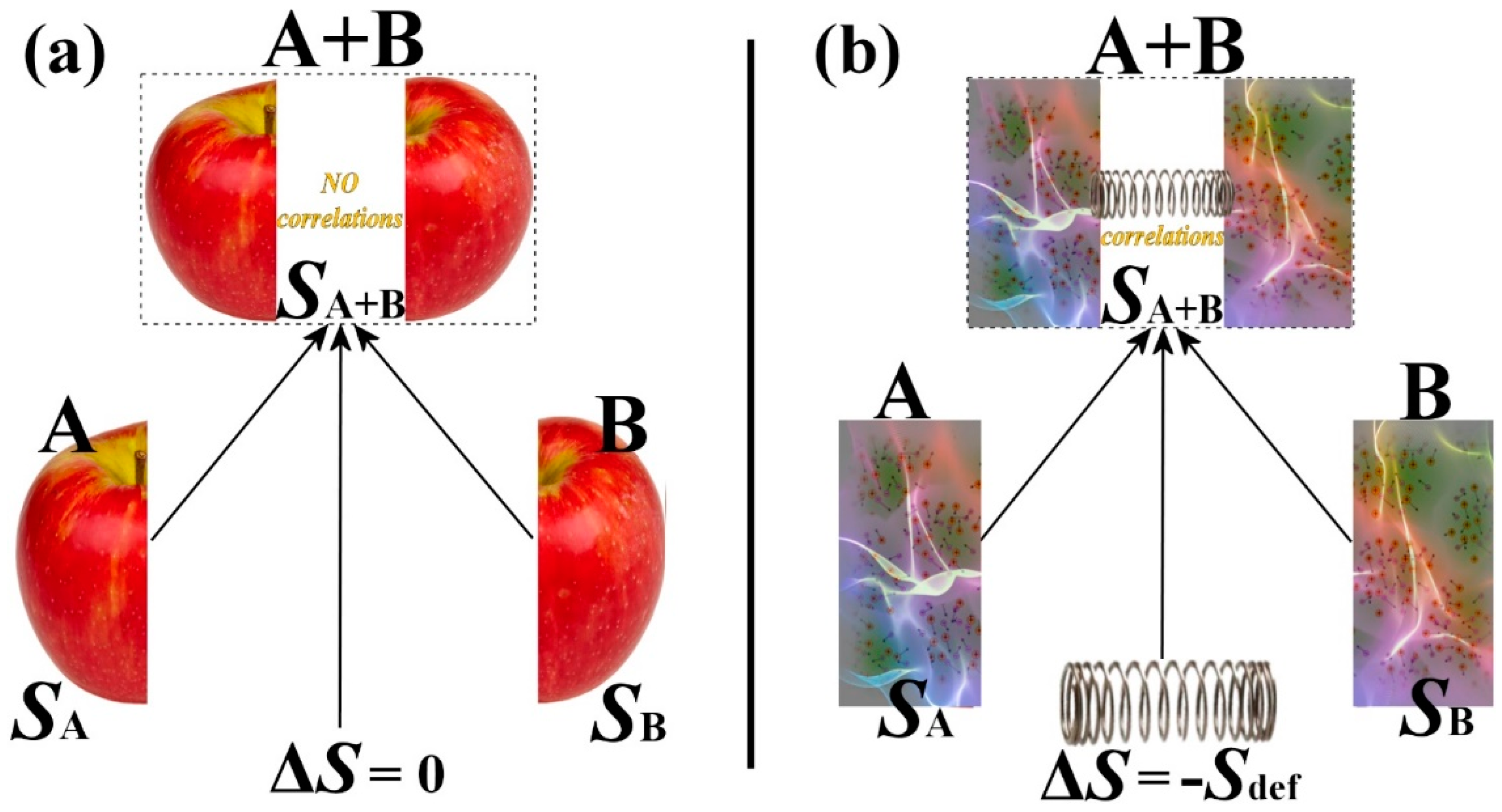
Entropy | Free Full-Text | Thermodynamic Definitions of Temperature and Kappa and Introduction of the Entropy Defect

The molar specific heat at constant pressure of an ideal gas is (7/2) R. the ratio of specific heat at constant pressure to that at constant volume is
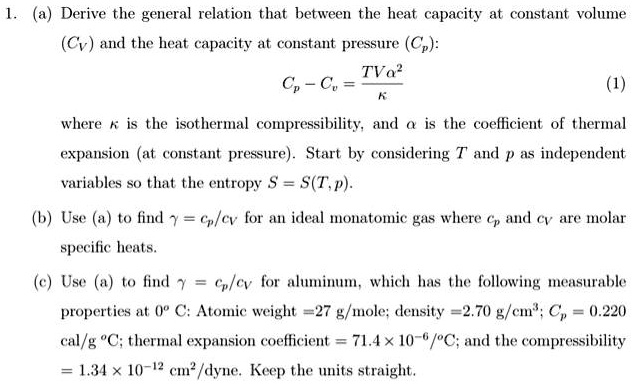
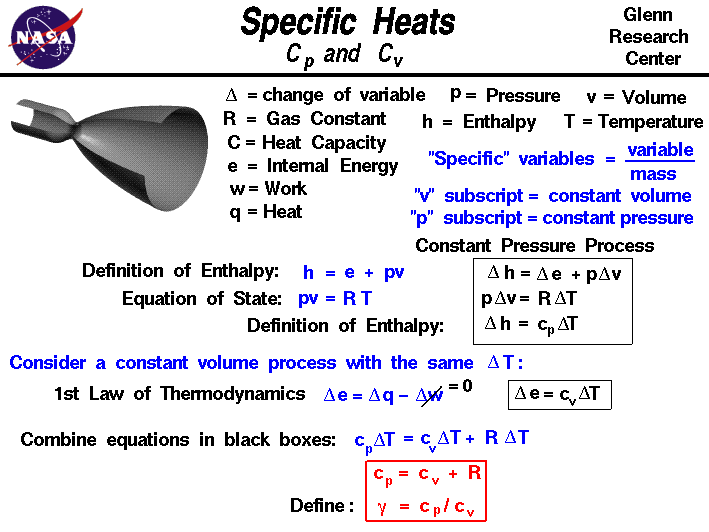
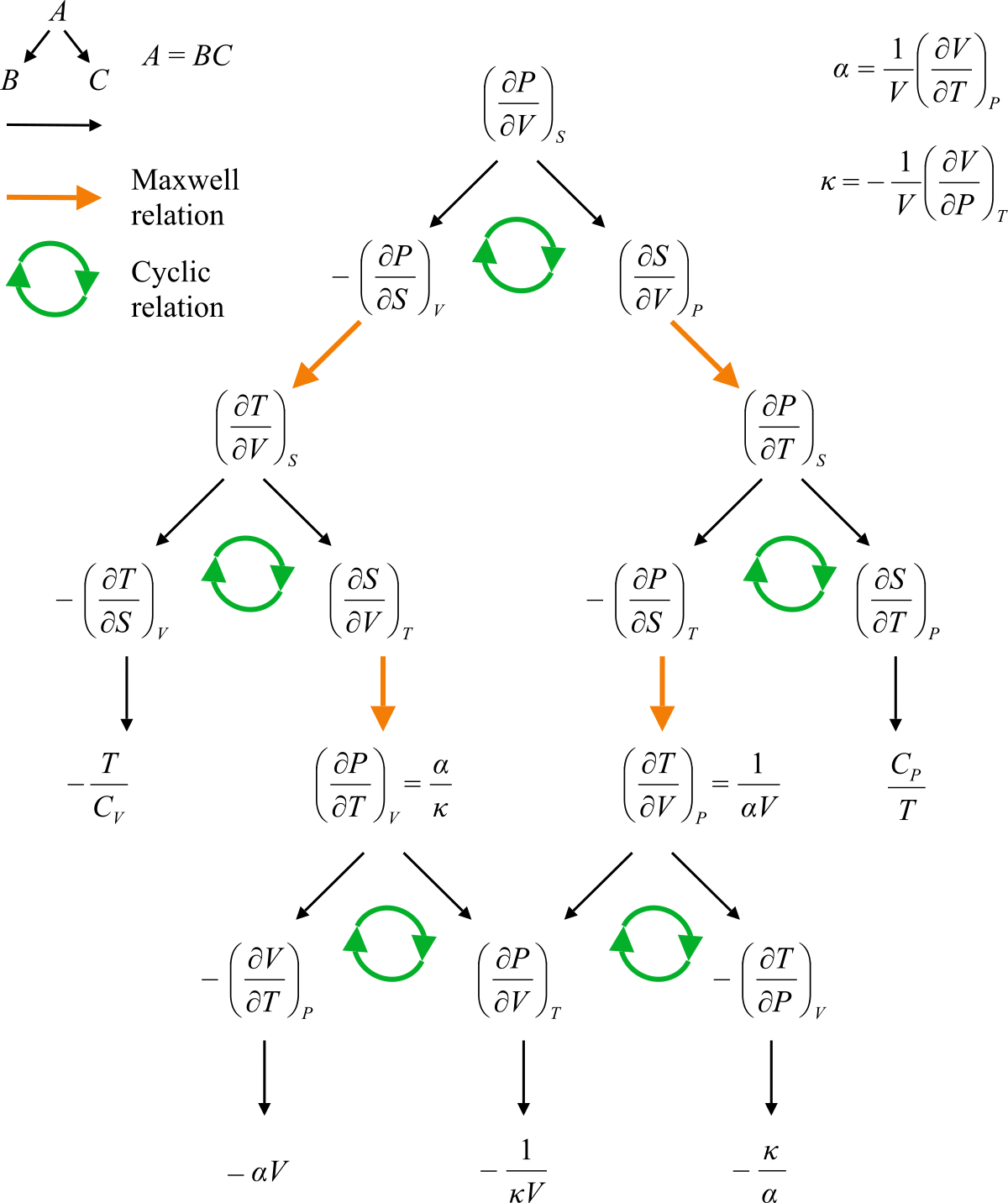
SOLVED: (a) Derive the general relation that between the heat capacity at constant volume (Cv) and the heat capacity at constant pressure (Cp): TVo? C" where #is the isothermal compressibility, and is

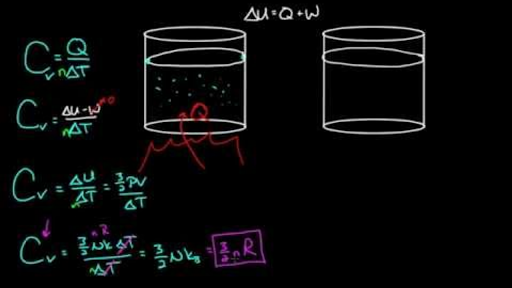
For an ideal gas the molar heat capacity varies as C = CV + 3aT^2 . Find the equation of the process in the variables (T,V) where a is a constant.
Derivation of unifying formulae for convective heat transfer in compressible flow fields | Scientific Reports

Specific heat capacity (cv) at constant volume vs. temperature (T) for Ni. | Download Scientific Diagram

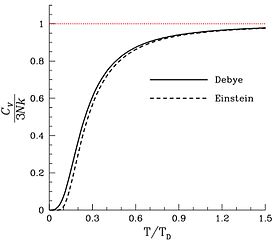
Variation of the constant volume heat capacity C V with the ratio of T... | Download Scientific Diagram
![SOLVED: [6 marks] This problem gives practice with taking derivatives! The isothermal compressibility Kr (kappa) describes how the volume of a substance changes with pressure at constant temperature. Given Page of 3 SOLVED: [6 marks] This problem gives practice with taking derivatives! The isothermal compressibility Kr (kappa) describes how the volume of a substance changes with pressure at constant temperature. Given Page of 3](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/8fd0309efe92472f8d87f1bd77df5223.jpg)
SOLVED: [6 marks] This problem gives practice with taking derivatives! The isothermal compressibility Kr (kappa) describes how the volume of a substance changes with pressure at constant temperature. Given Page of 3

Energy Conversion CHE 450/550. Ideal Gas Basics and Heat Capacities - I Ideal gas: – a theoretical gas composed of a set of non-interacting point particles. - ppt download

Variation of specific heat at a constant volume (C V ) with temperature... | Download Scientific Diagram

Molar Heat Capacity at Constant Volume for Isobutane at Temperatures from (114 to 345) K and at Pressures to 35 MPa | Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data

mu PT$$ statistical ensemble: systems with fluctuating energy, particle number, and volume | Scientific Reports